New RVC research reveals the extent of suboptimal vaccination practice in sheep and barriers to training for farmers
New research from the Royal Veterinary College has revealed the large extent of suboptimal vaccination practice in the UK sheep industry and the impact of the lack of awareness of training for farmers. The research also identified the barriers farmers face accessing training. This provides valuable information for the industry to help guide education of vaccination technique. This will ultimately improve technique and storage, enhancing vaccination efficacy, animal welfare and reduce disease. It could also help prevent wastage of valuable cuts of meat, improve sustainability and increase small margins for farmers.

Vaccines are commonly used in sheep farming to protect flocks from a variety of diseases, an important practice, given in 2021 DEFRA recorded that the UK national breeding flock comprised of 14.5 million sheep. However, the prevalence of suboptimal technique is widely unknown in the industry, which can result in less effective vaccinations and potential harm to animal welfare, including injection site lesions.
The RVC research team, led by Lauren Hall, a newly qualified Veterinarian, alongside Beth Reilly, Teaching Fellow in Clinical Farm Animal Management and Dr Nicola Blackie, Senior Lecturer in Production Animal Science, set out to raise awareness of this important issue. In doing so, they conducted an online survey which was distributed to UK sheep farmers, asking about their vaccination technique and storage, which was studied in relation to training.
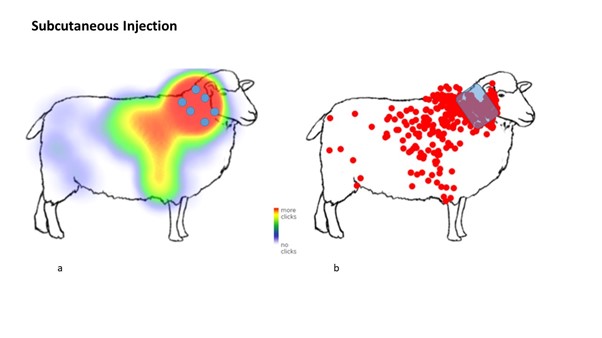
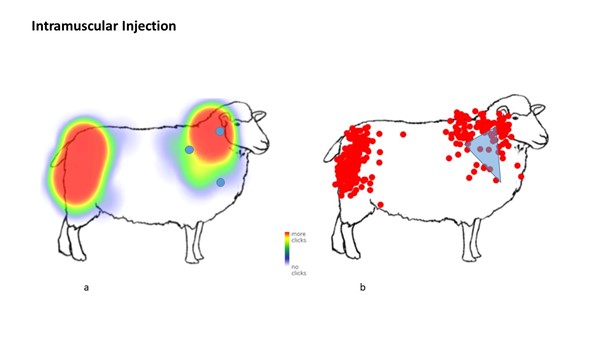
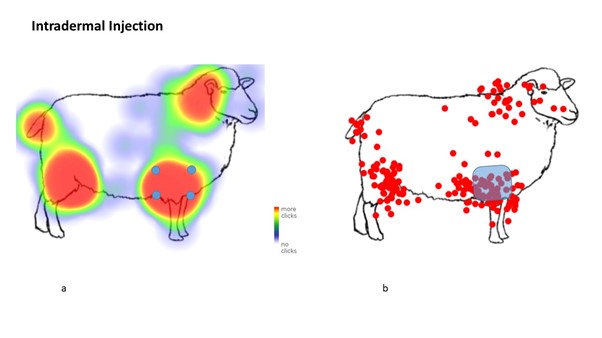
From the 370 respondents, the survey found that only 26.1% of participants correctly identified the correct location for subcutaneous (under the skin), 38.0% for intra-dermal (into the skin) and 7.7% for intramuscular (into the muscle) vaccination administration.
The study also revealed that just 45.5% of respondents stored vaccines in a fridge specific to veterinary medicines, 33.9% used a temperature logger and 6.4% undertook daily fridge temperature checks. In addition, 45.5% of respondents kept vaccines 48 hours or longer after first use and 11.1% kept them until the next time they planned to vaccinate. Incorrectly stored and broached vaccines may result in ineffective vaccination of sheep. Vaccine procedures are implemented based on farm disease risk so consequentially animal welfare may be inadvertently compromised.
Additional key findings include that:
- 8% of farmers buy their vaccines from an agricultural merchant while 29.1% purchase them from their vet
- Only 10.1% of farmers learnt how to vaccinate from their farm merchant, 48.1% from their vet and 44.4% from an associate – indicating a key gap and opportunity to improve practice through training
- Only 43.7% of farmers received training in vaccinations however, this was due more to barriers than a reluctance to training with 83.9% of respondents stating they would consider attending a course in person or online to improve their knowledge of the safe use of medicines.
The study also further considered the barriers to training and identified these to be time (45.6%); money (35.8%); not being aware training courses existed (34.8%); feeling they already knew how to vaccinate safely and effectively (40.7%). Additionally, 73.9% of respondents were unaware of any training courses they could attend, highlighting the need for advertising and promoting training within the industry.
The study calls for more consistent messages on vaccination technique and streamlining of training within the industry. It also highlights a need for more options for vaccination training to be clearly available to farmers. In addition, it highlights the opportunities that vets have to support the improvement of vaccination techniques and storage through training farmers and even the potential for interprofessional collaboration to bridge this knowledge gap.
Dr Nicola Blackie, Senior Lecturer in Production Animal Science at the RVC, said:
“Suboptimal vaccination technique is not due to unwillingness to attend training but more needs to be done to promote and reach the farmers.
“There is evidence that suboptimal vaccination technique is potentially occurring on UK sheep farms. For all injection types, a wide range of vaccination locations were indicated and a majority improperly administered or stored vaccines.”
 |
 |
 |
Notes to Editors
Reference
Hall LE, Reilly B, Blackie N. Surveying UK sheep farmers’ vaccination techniques and the impact of vaccination training. Vet Rec. 2022;e1798.https://doi.org/10.1002/vetr.1798
The full paper is available from 21st July 2022 and can be accessed here: https://doi.org/10.1002/vetr.1798
PDF Link: https://bvajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/vetr.1798
For media enquiries, please contact:
- Jasmin De Vivo jasmin.devivo@plmr.co.uk or rvc@plmr.co.uk
- Press Line: 0800 368 9520
About the Royal Veterinary College
- The Royal Veterinary College (RVC) is the UK's largest and longest established independent veterinary school and is a Member Institution of the University of London.
- It is one of the few veterinary schools in the world that hold accreditations from the RCVS in the UK (with reciprocal recognition from the AVBC for Australasia, the VCI for Ireland and the SAVC for South Africa), the EAEVE in the EU, and the AVMA in the USA and Canada.
- The RVC is ranked as the top veterinary school in the world in line QS World University Rankings by subject, 2022.
- The RVC offers undergraduate and postgraduate programmes in veterinary medicine, veterinary nursing and biological sciences.
- A research led institution with 88% of its research rated as internationally excellent or world class in the Research Excellence Framework 2021.
- The RVC provides animal owners and the veterinary profession with access to expert veterinary care and advice through its teaching hospitals and first opinion practices in London and Hertfordshire.
You may also be interested in:
-
New research from the RVC highlights pandemic risks posed by evolving swine flu viruses in Europe
A new study led by the Royal Veterinary College (RVC) has revealed significant genetic and …

